Published on 1 December 2022
Contents
2. Contributing to Belfast’s ambition
- The Belfast Agenda
- Belfast Bolder Vision
- Belfast Resilience Strategy
- Future City Centre programme
- Belfast Economic Strategy 2022 to 2030
- Belfast Region City Deal
3. Building our urban innovation ecosystem
- Collaborative leadership
- Urban challenges
- A focus on the citizen
- A vibrant innovation economy
- Data environment
- Financing, procurement and adoption
- Technology infrastructure;
- Place-making
- Citizen opportunities for digital innovation
- Maritime Mile Innovation Hub
- Amplitude: Wireless Belfast
- Urban innovation for Net Zero
- Belfast urban data ecosystem
- Growing healthy urban neighbourhoods
- Accelerating the SME Innovation Ecosystem
- Augment the city
- Supporting advanced urban services
1. Foreword
Digital innovation is having a profound effect on our economy, our city and on our lives. This impact is sometimes obvious, for example, the influence of online retail on traditional ‘bricks and mortar’ businesses or the way the mobile phone has changed how we consume our entertainment. And there are times when the impact is less immediately obvious, such as the growing influence of AI algorithms. As city leaders, we have ambitions to steer Belfast towards a successful and sustainable future, as outlined in our community plan, The Belfast Agenda. We have a responsibility to consider the impact of digital innovation on our city, our citizens and visitors, and on the services we design and deliver. It has vast potential as a force for good to help us deliver on this agenda. It offers many new opportunities that will have a hugely positive impact on society. But it also has the potential to be disruptive in ways we can’t predict. The Smart Belfast Urban Innovation Framework is an acknowledgement by Belfast City Council that as civic leaders we cannot ignore the impact and potential disruption of digital technology. Indeed, we have a responsibility to work with our partners from industry, academia and wider society, to harness digital innovation for the common good.
Smart Belfast is about making sure that together we put in place the conditions for collaborative innovation that will maximise the positive impact of technologies in our city. In this new framework we describe the common ‘pillars’ that we believe Belfast, collectively, must have in place to make this urban innovation ecosystem a reality.
We also set out Belfast City Council’s specific contribution to this ecosystem. Our programme of work, to be delivered within our Smart District, is designed to contribute to the city’s strategic ambitions and also contribute to these shared ecosystem pillars.
On behalf of Belfast City Council, I would like to acknowledge the many individuals and organisations from across the public, academic, community and private sectors who have contributed to the development of this framework and who continue to make Belfast a truly exciting place to innovate for the future. At the beating heart of Smart Belfast is collaboration, and we look forward to working with you to deliver on the city’s ambitions.

Councillor Emmet McDonough-Brown
Chairperson of Strategic
Policy and Resources Committee Belfast City Council
Delivering on the ambitions of the city

Smart Belfast is based on the understanding that digital innovation has an increasingly dominant role to play in both urban, social and economic policy. Our ambition is to find ways to harness this innovation to better support Belfast’s transformation to a more productive and sustainable city that provides a rich quality of life for our citizens.
First devised in 2017, the Smart Belfast Urban Innovation framework nurtures an environment in which innovators from across industry, academia, the public sector and from our communities can work together to find new ways to address Belfast’s major urban and economic challenges.
Smart Belfast is constructed around the concept of ‘urban innovation’. Rather than restrict the idea of innovation to a purely economic or business development agenda, we argue that there is an important, mutually beneficial interplay between growing our innovation economy and exploiting digital innovation to address major urban policy issues. These include the city’s response to climate change, healthy living, sustainable urban mobility and economic transformation.
Our new framework, which runs to 2026, incorporates many important ideas that have emerged over the past few years, not least of which has been learning from society’s response to the global pandemic.
We have also sought to find ways to maximise the opportunities offered by the £120 million Belfast Region City Deal digital investments that are planned for the coming decade. Our new approach acknowledges the exciting potential of new initiatives such as the Innovation City Belfast partnership.
Our refreshed framework puts much greater emphasis on the importance of place and place-making to urban innovation - an approach that has resulted in the council’s commitment to a Smart District right in the heart of the city.
Urban innovation is a collective effort. Belfast City Council can offer a leadership and convening role, but ultimately, partners and communities across the city need to work together to cultivate an urban innovation culture and ecosystem. As such we very much welcome the enthusiasm and support that Smart Belfast has received.
City Innovation Office
Belfast City Council
Smart Belfast 2017-2021: Key Deliverables
The first Smart Belfast Framework was developed by Belfast City Council’s City Innovation Office in 2017. It delivered a range of projects, attracted substantial investment, and influenced the wider conversation about the impact of digital technologies on our city’s future.
The City Innovation Office has:
- Leveraged over £10 million of investment.
- Delivered 47 innovation projects.
- Worked with over 200 SMEs and stakeholders.
- Hosted over 30 events with 4,100 participants.
- Attracted $1 million to establish the Belfast Office for Resilience.
- Built Northern Ireland’s first free-to-use Internet of Things network.
- Showcased the best of Belfast at five international tech conferences.
- Developed a £120 million digital investment business case for the Belfast Region City Deal.
- Brought forward recommendations for the establishment of a Belfast Digital Innovation Commissioner.
- Informed the design and initiation of Innovation City Belfast, the innovation partnership of city institutions.
- Worked with Government to establish the Digital Catapult’s Immersive Lab NI.
- Established a unique Smart Cities partnership with the South Korean City of Sejong.
Endorsements
Through the original Smart Belfast Framework, place leaders in Belfast demonstrated the tremendous power of civic innovation challenges to spark new solutions in place-based services. Many businesses and citizens have benefitted from this pioneering approach to market engagement and public contracting. Based on that foundation, the city and region has rightly established a reputation as a leading UK hub of innovation. Connected Places Catapult is delighted to have played a part in supporting Belfast on this journey and commends this new iteration of the Framework and all that it promises to do to extend Belfast’s place as an engine of innovation and growth.
Professor Greg Clark CBE, Chair of Connected Places Catapult
The RSA has been at the heart of social impact for over 260 years, so I am delighted to support Smart Belfast’s Urban Innovation Framework. We are particularly excited to see its focus on engaging through citizen participation and city stakeholders from all areas of society. The framework provides a sound foundation for Belfast’s innovation and digital transformation.
Patrick Hurley, Northern Ireland Manager, Royal Society for Arts, Manufactures and Commerce
I am delighted to support the Smart Belfast Urban Innovation Framework. Belfast Chamber is really interested in how businesses can benefit from the establishment of a Smart District which will provide the opportunity for businesses to trial and test new products and services in real world situations. We welcome the ambition to ensure Belfast businesses have access to the latest technology platforms and advanced wireless infrastructure.
Simon Hamilton, Chief Executive of Belfast Chamber of Trade and Commerce
I am delighted to offer an endorsement for the Smart Belfast Urban Innovation Framework. It sets out some of the key ingredients to help strengthen Belfast’s innovation ecosystem. The challenge approach provides the opportunity for our growing sectoral clusters to respond with relevant solutions to urban problems. The framework acknowledges the importance of citizen participation and ensures that an inclusive approach is at the heart of the digital transformation plans for the city.
Steve Orr, Chief Executive, Catalyst
The nature of digital technology is such that its impact will be felt right across all aspects of our society. It’s important that individuals and communities are at the heart of ensuring tech is a force for positive impact. I’m pleased to see that Smart Belfast has integrated collaboration and inclusion with the citizen into its approach.
Roisin Woods, Chief Executive Officer, Community Foundation NI
Belfast’s digital innovation strengths
- Belfast identified as one of the world’s top 10 Digital Economies of the Future (the only UK city other than London).
- Second-fastest growing knowledge economy region in UK.
- Number one international investment location for US cybersecurity development projects.
- Number one global destination for financial technology investment.
- Number one European destination city for new medical software development projects.
- Northern Ireland is best place to work in digital in the UK (by salary to cost of living).
- In 2019, 26 per cent of all job openings in Belfast were in digital technology - the highest in UK.
- There was a 300 per cent increase in research and development (R and D) investment by local businesses over the last decade.
- Venture capital funding increased tenfold over the last decade.
- Our universities are in the top 20 universities in UK.





2. Contributing to Belfast’s ambition
It is a significant period for Belfast. The city is emerging from the COVID-19 pandemic whilst also facing a cost-of-living crisis. Alongside designing here-and-now responses to these immediate challenges, the city is also developing long term plans that will put in place the investments required to address the challenges generated by the wider global economic transformation and the need to respond to climate change.
Urban innovation has much to offer to help tackle these challenges. They are so significant they will require novel solutions, risk-taking and a commitment to cross-sector collaboration. Urban innovation also has an exciting and necessary contribution to off in Belfast’s transformational journey towards sustainability and global success.
In this section, we outline key plans and strategies where we believe urban innovation has a particularly important role to play.
The Belfast Agenda
-2.jpg?width=114&height=150)
First published in 2017, the city’s community plan, The Belfast Agenda, has been refreshed with a roadmap for action over the next four years. The Agenda recognises the importance of high-quality places where communities can thrive; and the need to work in partnership to build an inclusive, sustainable, culturally vibrant, healthy and connected city which offers opportunities for all.
Our focus over the next four years are:
- Our people and communities - Making life better for all our residents.
- Our economy - Creating inclusive and sustainable growth, learning and opportunity.
- Our place - Creating a liveable and connected, vibrant and competitive city.
- Our environment - Creating a net-zero emissions and climate-resilient city.
Belfast Bolder Vision

Belfast has developed a shared approach to creating a more attractive, accessible, safe and vibrant city. Developed jointly with the NI Department for Communities and the NI Department for Infrastructure, it reflects that the changes that need to happen to ensure economic and environmental resilience are embedded within the liveability and mobility landscape of Belfast.
The Bolder Vision has identified several ‘Key Moves’ where partners need to intervene to transform critical parts of the city to create a green, people focused, connected city centre:
- Create a Civic Spine - establish a clearly defined and recognisable north-south civic route to provide safe and accessible movement through the city centre, including car-free streets.
- Reimagine the Inner Ring Road and End Car Dominance - transform the ‘inner ring’ to reduce physical severance for surrounding communities and become a sustainable mobility corridor.
- Promote City Centre Living - encourage city centre living by providing greater quality, choice and affordability of accommodation. Establish a city-wide network of people friendly routes and city parks.
- Embrace the River Lagan and Waterfront - enhance existing, and create new, riverside attractions to encourage better use of the River Lagan. Strengthen connections between the river and the city centre.
Digital innovation has a significant contribution to make in achieving the Bolder Vision. In particular the Smart District, which will be coterminous with the city centre, offers a rich, unique environment in which to innovate with communities, businesses, universities, colleges and planners.
Belfast Resilience Strategy

The Resilience Strategy is the city’s first climate plan. It sets out 30 transformational programmes to transition Belfast to an inclusive, zero-emissions, climate-resilient economy within a generation. It provides a framework to safeguard Belfast against situations that could threaten its safety and stability over the coming years and helps us deliver our Belfast Agenda priorities.
Areas of focus include:
- Climate adaption and mitigation.
- Participation of children and young people.
- Connected, net-zero-emissions economy.
The strategy’s companion, the Belfast Net Zero Carbon Roadmap, has set a 2025 target of a 66 per cent reduction in CO2 emissions from their 2000 levels. The roadmap’s authors note that this challenging target will require a suite of innovative solutions.
Future City Centre programme

The programme seeks to address challenges facing Belfast city centre including the changing retail, tourism and hospitality landscape and the need to re-imagine and diversify to future-proof the city centre.
Future City Centre addresses the importance of vitality, the diversification of land, promoting mixed uses, open and green spaces and community infrastructure. Key work strands include:
- Physical regeneration and environmental improvements
- City centre vitality
- Addressing vacancies
- Positioning the city to compete
- Business support and digital innovation
- Policy
Belfast Economic Strategy 2022-2030

This strategy aims to support the sustainable and inclusive growth ambitions for the city. It aligns with the Northern Ireland Department for the Economy’s economic vision ‘the 10X Economy - Northern Ireland’s decade of innovation’.
The strategy focuses on how the city can maximise the return on investments to benefit all our citizens.
It includes a detailed action plan which defines the role of the council and other key stakeholders in driving forward growth in the short, medium, and long-term.
Belfast Region City Deal

A once in a lifetime package of strategic regional investments, the City Deal is designed to foster:
Inclusive economic growth that delivers more and better jobs, a positive impact on the most deprived communities and a balanced spread of benefits across the region.
Partners include Belfast City Council, five partner councils, the two local universities and four of the region’s further education colleges. Together they are investing in digital innovation, tourism and regeneration, infrastructure and employability and skills.
The ‘Smart Belfast’ concept has greatly influenced the nature of the digital investments.
Our urban innovation programme has been designed in part to maximise the impact of these investments:
- A £55 million Challenge Fund programme will focus on a range of missions designed to address the regional grand challenges of Artificial Intelligence, Health and Wellbeing and Sustainability and Resilience.
- A £39.5 million Enabling Infrastructure Fund will support the development of the Belfast Smart District and a regional testbed network through investment in world-class digital connectivity and data infrastructure.
- A network of Regional Innovation Hubs will ensure diffusion of innovation and skills throughout the region, and further build on regional strengths in key sectors such as advanced manufacturing.
3. Building our urban innovation ecosystem
Cities that have been most successful in adopting innovation to support their wider strategic ambitions, have established an enabling environment that encourages a culture of collaboration between many institutions and individuals.
Every city is different but there are ‘pillars’ that are common to most urban innovation ecosystems. Looking at good practice worldwide and drawing from our own hard-won experience, we have identified a set of pillars that will make Belfast better equipped to develop and deploy novel solutions to complex challenges, while at the same time making our city one of the world’s most attractive locations for innovation investment.
The good news is that Belfast has many of the ingredients of each pillar already in place. In the following section we set out what needs to be done by all partners to grow from this position of strength, to ensure that our city is ready for the challenges of the coming decade.
3.1 Collaborative leadership
Cities that have been most successful in harnessing urban innovation foster an innovation culture within organisations and between organisations. They often set up a strategic partnership to act as a champion for this culture, building collaborations between sectors and across boundaries.
A ‘quadruple helix’ model brings industry, academia, communities and public institutions together to find opportunities for collaborative gain. They adopt an agile, data-driven, citizen-led approach that is open to experimentation, risk-taking and is highly responsive to rapid change.
Innovation City Belfast, of which Belfast City Council is a founding partner, is building such a partnership to establish Belfast as a globally significant destination for innovation that can directly contribute to the city’s major economic, social and environmental challenges.
Key partner tasks
- Identify and align Belfast’s policy priorities with digital innovation opportunities - particularly in relation to urban development and our climate ambitions.
- Develop an agile delivery vehicle to facilitate public/private co-investment in urban innovation projects.
- Develop mechanisms to facilitate a citizen co- design approach and provide ethical oversight for digital innovation projects.
- Support the development of city-level intelligence to aid prioritisation and to measure impact.
- Create a shared Belfast urban innovation investment proposition that we can proudly promote to the world.
3.2. Urban challenges
A ‘challenge’ or ‘mission’-led approach has been adopted by many governments and institutions across the world. Such an approach recognises the limitations of traditional public policy interventions and procurement in tackling some of the more intractable problems in society. It seeks to use other means to co-opt industry and academia to work with government and communities in co-designing innovative solutions to these challenges, while at the same time using these challenges as a spur for greater public and private sector investment in sustainable innovation and R and D.
Belfast and Northern Ireland have previously adopted elements of this approach - including Smart Belfast, the Department for the Economy’s Small Business Research Initiative (SBRI) programme, and the Belfast Region City Deal partnership.
Key partner tasks
- Build capacity amongst city partners (including the SME sector, public bodies, communities and university research partners) to support participation in challenge-led programmes.
- Work with city leaders to define specific challenge areas aligned to urban policy priorities particularly in relation to the city’s economic, environmental and societal ambitions.
- Work with Belfast Region City Deal partners to design and deliver the £34m mission-orientated Innovation for Societal Impact fund.
- Public bodies to fully harness Northern Ireland’s Small Business Research Initiative programme to stimulate innovation in public procurement.
Innovation City Belfast
The leaders of seven of the city’s key institutions; Belfast City Council, Belfast Harbour, Catalyst, Queen’s University Belfast, Ulster University and Belfast Met, with Invest NI as an advisory partner, have formed a partnership to drive a shared digital innovation ambition for the city.
Its key objectives include:
- Influencing regional and UK policy and programmes.
- Attracting substantial new public and private sector investment in innovation.
- Supporting the rapid growth of high potential knowledge economy clusters.
- Supporting a skills agenda that prepares our workforce for the future economy
- Developing place-based innovation ecosystems.
- Maximising the economic and social impact of the Belfast Region City Deal innovation and digital investments.
3.3 A focus on the citizen
The citizen sits at the heart of Belfast’s ambitions. In a complex and increasingly data-enabled world, it is important that communities and city institutions can work together to understand the impact of digital technologies on our lives and society, and to build our capacity to utilise these technologies for the benefit of all. The active involvement of individuals and communities is key to identifying urban challenges, and in developing sustainable impactful solutions.
Key partner tasks
- Deliver an engagement programme to raise awareness of urban innovation, co-design methodologies, and the impact of digital technologies on cities.
- Design and deliver Citizen Opportunities for Digital Innovation (CODI), a capacity-building programme to create awareness, build capacity and establish processes to support citizen co-design on urban innovation projects.
- Work with community development and university partners to support place-based urban innovation initiatives.
- Develop a Belfast-focused shared resource to support current and proposed Living Labs in the city to ensure the design and delivery of a portfolio of collaborative innovation projects in the Smart District.
3.4 A vibrant innovation economy
The engine for digital innovation is a modern, sustainable knowledge economy. Without a critical density of talent, start-ups, entrepreneurs, innovators and engaged industry partners, Belfast would struggle to harness urban innovation.
Fortunately, our city has enviable strengths to draw upon. We are home to a vibrant tech sector, a workforce with world-class educational attainment, and a growing skills pipeline that is responsive to the needs of a modern economy.
We have globally recognised centres of research excellence and strong digital economy clusters in areas such as creative digital, fintech, cybersecurity and software development, with emerging clusters in life and health sciences.
Belfast needs to consider more broadly the specific implications of radical technological change on our economy, on businesses, on jobs and its potential to exacerbate economic exclusion.
Key partner tasks
- Deliver the Belfast Smart District as a testbed environment to accelerate translation research, and the development and adoption of digital and data-driven technologies to tackle urban challenges.
- Work with partners, including the Skills programme of Belfast Region City Deal and the Belfast Labour Market Partnership, to prepare our citizens, businesses and wider society for the disruption and opportunities associated with digital innovation.
- Work with Innovation City Belfast on the development of the Belfast Innovation District which aims to support high growth SME clusters that are important to our future economic success.
- Work with Innovation City Belfast on the design and delivery of an Inclusive Innovation programme to support communities to access and benefit from the success of a growing innovation economy.
- Develop a shared platform to better engage with SMEs and entrepreneurs, providing targeted support.
- Work with partners on an insights and impact platform to support the design of interventions, measure their impact, and provide quantitative evidence for investors and funders.
- Identify and develop models of funding to align societal challenges with cluster growth, research and innovation projects.
3.5 Data environment
Data is a fundamental asset for digital transformation and a key element in driving forward Belfast’s innovation economy. The decline in the cost of data collection, storage and analysis, is leading to the generation of huge volumes of data, often referred to as ‘big data’.
Such data is the basis for new industries and products, supports world-class research and creates significant competitive advantages. It also plays a major role in understanding and addressing societal challenges and designing new and better public services.
There are existing limitations which prevent Belfast from realising the full potential of our data. These include insufficient analytics capability, a lack of understanding of data as an asset, limited data sharing, poor interoperability and data quality as well as a lack of necessary skills and data literacy, and a sluggish data governance environment. There is also an increasing lack of trust from the public in the collection and use of data.
Key partner tasks
- Promotion and adoption of a common set of data principles to support urban innovation and the delivery of the Belfast Region City Deal digital programme.
- Enhance data leadership particularly amongst public sector bodies and community planning partners.
- Work with Open Data NI and others to encourage the generation, publication and utilisation of open data to address societal challenges.
- Encourage use of open standards and promote interoperability between urban data systems in the city.
- Develop and enhance data skills and capability in the public sector and communities.
- Develop a shared urban data environment for businesses, citizens, academia and the public sector that supports collaborative innovation on urban challenges and the delivery of enhanced public services.
- Work with partners, UK regulators and relevant networks to create a ‘data sandbox’ environment to support the novel use of data in the public realm.
3.6 Financing, procurement and adoption
Investment in innovation and research and development (R&D) is a defi characteristic of successful modern economies. It allows companies to adopt new ideas; it provides opportunities for SMEs to take risks and grow; and it supports research in our universities and colleges.
While NI business investment in R and D has grown, it’s been from a low base compared to other UK regions. Nesta’s ‘The Missing £4 billion’ report suggests our region has missed out on UK government R and D investment.
Our SMEs have struggled to navigate an overly complex funding landscape. And some have noted that it has been difficult locally to attract funding for their next stage of growth beyond the ‘first million pounds’.
The public sector can play an important role as first customer and champion, but the region’s public procurement requirements often represent a challenging hurdle for smaller companies.
The lack of access to ‘real world’ testbed environments also denies companies the opportunity to develop, test and scale solutions, and showcase to potential buyers. This environment is fundamental for de-risking innovation, accelerating adoption and facilitating routes to commercialisation.
Key partner tasks
- Develop and deliver the £20 million Belfast Region City Deal Digital Innovation Venture Fund.
- Work with Innovation City Belfast to attract greater UK Government innovation investment.
- Establish a programme to enhance innovative public procurement and adoption of innovation solutions amongst the city’s institutions that also maximises community benefit
- Develop a vehicle to facilitate public and private sector co-investment in smart city projects.
- Develop an ‘access to finance' platform to support SMEs, fund designers and public policy managers to reduce administrative burdens and provide clarity of the funding landscape.
3.7 Technology infrastructure
The UK Digital Strategy notes that ‘for businesses to thrive and grow, government needs to create the conditions and set the framework for investment in widespread and up-to-date infrastructure.’
Digital innovation is dependent on the existence of accessible, world-class digital connectivity and data infrastructure that is secure and reliable. Collaborative innovation flourishes best in a technological environment that encourages open systems, open interfaces, open data and the use of open source software.
Urban data platforms, and the open data ecosystems in which they exist, are designed to unlock data to support city services and understanding urban challenges.
Key partner tasks
- Develop a shared open city architecture for technology to guide adoption and procurement.
- Work with partners to shape the focus and potential of the £39.5 million Infrastructure Enabling Fund as part of the Belfast Region City Deal.
- Deliver an advanced wireless investment proposition for the region funded through the Belfast Region City Deal.
- Develop and deliver a £5 million urban data platform enabling industry, academia and the public sector to generate, manage and analyse data in ways that spur collaboration and open innovation.
- Deliver the Belfast Smart District as a testbed where new, emerging technologies can demonstrate their potential to address societal challenges and inform future policy and interventions.
- Support the development of digital twins to enhance the planning and management of urban systems including mobility and energy systems.
- Incorporate the UK Connected Places Cyber Security Principles into the development of connected places in Belfast.
3.8 Place-making
To fully harness the potential of urban innovation, Belfast needs to take a ‘whole-place’ perspective that recognises the city’s unique historical and geographical characteristics and the role these play in supporting our innovation ambitions.
While innovation strategies often focus on elements such as skills, business development and enabling digital infrastructure, there are also place-based elements that are equally important in the innovation mix. We need to address factors such as the quality of life, housing, mobility, and our cultural and retail offerings. A thriving and creative city is the best place to enable urban innovation to spark.
The development of smart and innovation districts are an important approach for much of this work as they firmly ground innovation within real-world investments, challenges and opportunities. But success depends on their relationship with the wider city and how the benefit and opportunities that accrue in these locations can be accessed by citizens and communities. There are successful examples of such ‘whole place’ approaches in cities across the world including Barcelona, Berlin, Stockholm and Toronto.
Key partner tasks
- Design and implement the Belfast Smart District to support the future of our city centre and the wider adoption of digital innovation in addressing Belfast’s major urban challenges.
- Support the delivery of the city’s urban transformation ambitions - including the Bolder Vision, Spatial Plan and the Belfast Agenda by ensuring that opportunities for digital innovation is integrated into these key plans and strategies.
- Support Innovation City Belfast partners on the development of the Belfast Innovation District in the city’s Titanic Quarter and City Quays area to stimulate a community of high growth SME clusters built around research excellence that is connected to its local communities and the wider city.
4. Our programme of work
In the previous section, Building our urban innovation ecosystem, we described the shared pillars of urban innovation, and the collective actions that we believe city institutions needs to grow the urban innovation ecosystem. In this section we set out the specific initiatives that Belfast City Council’s City Innovation Office are committing to over the next four years.These initiatives are designed to maximise the impact of urban innovation on Belfast’s strategic priorities, while also making our own contribution to the ecosystem’s pillars. Each initiative has been identified based on these criteria:
- The initiative should be ‘challenge-led’, addressing urban issues where digital innovation can make a significant contribution.
- The initiative should contribute to the urban innovation pillars.
- The initiative should have the potential for replication or scaling across the city and wider region.
- The initiative is likely to require a collaborative, multi-disciplinary approach that can usually attract co-investment.
- The project should demonstrate a route to commercialisation or contribute to the city’s wider economic objectives.
Key to urban innovation pillars
1. Collaborative leadership
2. Urban challenges
3. The citizen
4. A vibrant innovation economy
5. Data environment
6. Financing, procurement and adoption
7. Technology infrastructure
8. Place-making
Citizen Opportunities for Digital Innovation (CODI)
CODI will explore how we can support our citizens and city innovators to better understand the role and impact of data and digital technologies on urban life, enabling citizens to actively participate in urban innovation to address issues that are important to them and shape the technological enabled city they live in.
CODI will utilise creative and interactive methods to explore topics such as co-design, citizen science, the Internet of Things, AI and data science, privacy, and smart cities. Learning from an initial pilot will inform proposals for a larger, longer term programme that will ensure citizens are at the heart of digital innovation projects within the Smart District and across the city.
Delivering for Belfast
- Enhance citizens’ awareness and understanding technology and data-enabled cities.
- Enhance community capacity to actively participate in the co-design of digital innovation to address local and city challenges
- Support potential pathways for individuals to transition to more formal training and education.
- Enable citizens to improve the design of public policy interventions through active involvement in digital innovation projects.
Investment for Belfast
- £70,000 for delivery of the CODI pilot.
- Planned over £1 million business case for a larger scale programme.
Collaborative partners
- Belfast’s community development sector
- Belfast’s community planning partners
- Belfast Metropolitan College
- Nesta Collective Intelligence unit
- Queen’s University
- Ulster University
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges
- 3. The citizen
Maritime Mile Innovation Hub
Belfast is working with seven European cities on a four-year programme that seeks to unlock the economic potential of historic urban areas. Together with the Maritime Belfast Trust, the local programme is focused on communities and neighbourhoods connected to Belfast’s Maritime Mile.
With €7.9 million funding from Horizon 2020, the programme will support skills and business development activities to create exciting opportunities for local innovative entrepreneurship. It is designed to take advantage of the Maritime Mile’s unique cultural and social offerings. Under the name ‘Hub-In’ - short for Hubs of Innovation - the programme will also explore new models for financing and accelerating local innovative start-ups.
Delivering for Belfast
- Challenge funding invested in local communities to support stimulate innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Enhanced innovation experience along the Maritime Mile.
- Increased footfall, dwell time and local spend.
- Enhanced local community skills in entrepreneurial and digital innovation.
- Develop a bank of transferable knowledge and toolkits for developing local community innovation initiatives across the city.
- Long term knowledge sharing with seven other European cities.
Investment for Belfast
- Over €680,000 invested in the city.
- Tailored technical expertise and advice from international partners.
- Collaborative partners
- Connected Places Catapult
- Creative Industries
- European Commission
- Maritime Belfast Trust
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges
- 3. The citizen
- 4. A vibrant innovation economy
- 6. Financing, procurement and adoption
Amplitude: Wireless Belfast
In the coming decade, advanced wireless networks will become the next generation backbone for innovative digital services. They will underpin the future of services in advanced manufacturing, connected health services, film-making, tourism, and retail. It’s estimated that wireless enabled services will be worth an additional £43 billion to the UK’s economy by 2030. The Amplitude programme will ensure that Belfast is ahead of its UK and Irish competitors in making our city the place for wireless innovation, investment and exploitation.
The programme will bring together world-class initiatives that are already planned or underway in our Smart District, our universities and businesses and demonstrate Belfast’s potential as a hub for wireless innovation. The aim is to grow further collaboration, attract additional research and private sector funding, and to encourage faster investment by the mobile industry itself. The programme will particularly focus on supporting easier access to advanced wireless services for our SMEs.
We are also working with planners, asset owners, and NI and UK governments on an action plan to reduce barriers to wireless network deployment. This will include establishing a one-stop-shop for mobile network service providers.
Finally, we are working with local partners to unlock specific locations including public sector assets, university campuses and other high demand areas to offer opportunities for developing innovative commercial models for wireless services.
Delivering for Belfast
- Faster deployment of advanced wireless services supporting enhanced SME innovation, productivity and competitiveness.
- Growth in successful research and SME grant applications.
- Greater access to mobile services across communities struggling for digital access.
Investment for Belfast
Up to £30 million Belfast Region City Deal investment.
Estimated £14 million direct economic benefit from proposed Belfast Region City Deal investments.
Co-investment by industry in innovative wireless research and development.
Collaborative partners
- Belfast Region City Deal
- Digital Catapult UK
- NI Department for the Economy
- Telecoms and networks industry
- Queen’s University
- UK Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport
- UK Telecoms Innovation Network (UKTIN)
- UK5G
- Ulster University
Pillar contribution
- 4. A vibrant innovation economy
- 7. Technology infrastructure
Advanced Wireless testbeds
As they roll out over the coming decade, advanced wireless networks will become the connectivity backbone for future digital services and innovations. Belfast has the opportunity right now to deploy small scale 5G testbeds, giving our industries, universities, colleges and SMEs the advantage of important early access to an innovative environment to develop, test and deploy new solutions.
Such testbeds will complement and enhance City Deal investments in areas such as digital twins, advanced manufacturing, immersive tech and connected health. We are working with City Deal partners, the wireless industry, public asset owners and university partners, to plan and deploy a supportive 5G environment that can offer important opportunities to explore inter-operability, open systems, and real-world deployment.
Urban Innovation for Net Zero
Belfast’s ambition to achieve carbon net zero by 2050 is a challenging undertaking. It is widely acknowledged that there are few avenues to success that don’t feature the radical and widespread adoption of digital innovation.
We are developing a joint programme of work with the council’s Climate Team to find ways to stimulate collaborative innovation in areas such as urban mobility and energy production, transmission and management.
Early strands of work are focusing on the use of novel data sources such as urban Internet of Things networks, data analytics and AI to construct better models and insights into the city’s existing carbon-dependent systems.
We will contribute directly to the Belfast Bolder Vision by supporting a more rapid shift to public transport and active travel options. This will include exploring micro-mobility solutions and transport alternatives, whilst supporting people to make improved sustainable travel choices. We will be guided across the Smart District by the ‘15-minute city’ concept.
We will build opportunities within the Belfast Smart District to harness the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact fund to encourage the region’s SMEs and universities to work together with the city region on significant net zero challenges.
Delivering for Belfast
- Contribution to a reduction in carbon emissions and improved resilience.
- Enabling citizens to understand their climate impacts and options.
- Better informed climate interventions. Supporting the sustainable, and just, energy transition whilst providing opportunities for local SMEs to innovate.
- Improved use of technology for environmental analysis and management.
Investment for Belfast
- Bids to the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund.
- Collaborative innovation funding from UKRI and elsewhere.
- Collaborative innovation investment from Industry.
Collaborative partners
- Belfast City Council departments
- Belfast Metropolitan College
- Belfast Region City Deal partners
- Met Office
- NI Government departments
- NI Statistics and Research Agency and other data sources
- Private sector organisations
- Queen’s University
- Ulster University
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges
- 7. Technology infrastructure
Belfast Urban Data Ecosystem
Recognising the underlying importance of data to urban systems and the innovation economy, this initiative focuses on those investments and activities necessary to foster a shared urban data ecosystem.
The programme builds on earlier work by Smart Belfast, and later by Belfast Region City Deal partners. It has a number of interconnected strands with privacy, security and open architecture being core characteristics running through our approach.
We will work with Belfast City Council departments to strengthen the organisation’s capacity to deliver on its civic leadership role in a data-enabled smart city. And we will work with regional partners to establish a Public Data Panel, the first of its kind in Northern Ireland. This will enhance the public’s understanding and direct involvement in the use of data for societal public benefit.
This work will be enhanced by the delivery of Citizen Opportunities for Digital Innovation.
Working with Belfast Region City Deal partners we will determine the specific digital investments required to support Belfast region’s urban data ecosystem. Building on previous work with Fraunhofer FOKUS, the study will design a £5 million City Deal business case to provide regional partners with the architecture and platform required to support collaborative data-enabled solutions, products and services.
Alongside these main strands of work, we will continue to deliver innovative opportunities to exploit data to contribute to specific city challenges. This includes challenge-focused hackathons and developing a complex digital twin of the city centre to provide fine-grain, real-time insights into its inter-connected social, environmental, physical and economic systems. The digital twin will be used to support innovation projects including multi-modal mobility, shared asset management, the future of the high street economy, and the growth of high-potential SME clusters.
Delivering for Belfast
- Enhanced data-led public policy making and service design.
- Greater SME access to urban data to unlock new business opportunities.
- Greater awareness and direct involvement by the public in urban data solutions.
- Contribution to key urban challenges associated with net zero targets.
- Greater efficiencies and innovation in the design and delivery of public services.
- Growth in successful research and SME grant applications
Investment for Belfast
- £100,000 from Belfast Region City Deal to deliver a feasibility study for an urban data platform.
- £5 million for Belfast Region City Deal partners to establish an urban data platform.
- Co-investment by industry partners in innovative data collaborations.
Collaborative partners
- Administrative Data Research Centre NI
- Belfast Region City Deal partners
- Information Commissioner's Office
- Nesta
- Northern Ireland Trust Research Centre
- Queen’s University
- Ulster University
Pillar contribution
- 4. A vibrant innovation economy
- 5. Data environment
Growing Healthy Urban Neighbourhoods
Belfast currently struggles with some of the worst health outcomes in the UK. The city is also facing demographic changes, with 40 per cent of its population projected to be over 50 by the mid- 2030s. These represent profound challenges for policy-makers, not only in the design of new health interventions, but also for planning, transport, housing and other urban services.
The Healthy Urban Neighbourhoods programme will collaborate with the city’s health sector, businesses, housing providers, community planning partners and universities to maximise the opportunities represented by urban innovation.
Within the Smart District, it is supporting projects that bring together local communities, SMEs that are developing innovative new health products, and university researchers. The approach provides opportunities for SMEs to work directly with end-users, while offering opportunities for individuals to trial new health technologies.
We are working with local universities on joint research funding applications that will extend this approach to include a ‘digital health hub’ in the Smart District alongside a challenge fund accelerator for health SMEs.
The programme also has ambitions to work with developers and planners to consider the requirements and integration of digital innovation within new housing developments in the city centre.
Delivering for Belfast
- Contribution to tackling loneliness in older people.
- Greater R and D investment by Belfast health SMEs.
- Contribution to the wider societal impact of major health research projects.
- Shaping long term urban capital investments to support health neighbourhoods.
Investment for Belfast
- A proportion of Connected Places Catapult’s £2.5 million Homes for Healthy Ageing testbed funding.
- Potential £15 million for digital health hub initiatives
- A proportion of the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund.
Collaborative partners
- Age NI
- Belfast Agenda partners
- Belfast City Council departments
- Belfast Region City Deal partners
- Community Development organisations
- Connected Places Catapult
- Health Innovation Research Alliance
- Health SMEs
- Health and Social Care Northern Ireland
- Queen’s University
- Ulster University
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges

Accelerating the SME Innovation ecosystem
At the centre of the Smart Belfast concept is the recognition that Belfast has a significant and growing innovation economy; one which is built upon the ingenuity, skill and hard work of our SMEs, start-ups and founders. Supporting this community, and find opportunities for collaboration that are mutually beneficial is key to the success of Smart Belfast.
Specific support for innovative SMEs therefore forms a substantial element of our programme going forward. We have sought to design this in ways that complement the extensive business development work by the council’s own Enterprise and Business Growth team, Invest NI, the Skills programme of the Belfast Region City Deal, and institutions such as Catalyst.
The most substantial strand is the collaboration with other Belfast Region City Deal partners to design and deliver radically new funding programmes that can support SMEs along their life cycle - whilst also ensuring that such programmes have a wider societal impact.
The key intervention is the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund supported by the Belfast Region City Deal. This fund will use a range of mechanisms, from small to medium sized grants through to more innovative challenge funding calls, to encourage greater investment in R and D by innovative SMEs.
Complementing this will be a £20 million Digital Innovation Venture Fund which will co-invest alongside the private sector in some of the region’s most exciting SMEs as they seek to grow into world-class companies.
Alongside these funding mechanisms are a series of other activities including developing new mechanisms for SMEs to navigate the complex public and private funding landscape; developing a shared platform to better engage with SMEs and entrepreneurs, providing more targeted support; using data analytics to allow partners to gain better insights into the potential for cluster and sector growth in our economy; and supporting policy-makers to better measure the impact of their economic development interventions.
Looking beyond the region, we also recognise the attraction of the concept of the Smart District to would-be investors and international collaborators. We will seek to use new and existing networks to build opportunities with cities including Sejong in South Korea, Smart Dublin and over one hundred smart cities worldwide.
Delivering for Belfast
- Growing the number of the city’s innovation SMEs.
- Contributing to growth in jobs.
- Increased investment by private sector in R and D.
- Strengthening Belfast as a place for foreign direct investment.
Investment for Belfast
- Proportion of £20 million for Digital Innovation Venture Fund.
- Proportion of £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund.
Collaborative partners
- Belfast Metropolitan College
- Belfast Region City Deal
- Digital Catapult UK
- Industry partners
- Innovation City Belfast
- Invest NI
Pillar contribution
- 4. A vibrant innovation economy
- 6. Financing, procurement and adoption

Augment the City
This initiative will bring together industry partners, our universities and the local creative digital sector to re-imagine the city centre experience. It will encourage the creative adoption of advanced wireless networking, cloud computing, and immersive technologies to create and showcase new opportunities for residents and visitors to explore our city’s stories, architecture and environment.
At the heart of Augment the City is a challenge fund competition designed to encourage university and local SMEs collaboration and investment.
Delivering for Belfast
- A major new immersive visitor experience in Belfast City Hall.
- Increased investment in R and D in the creative digital SMEs to grow their competitiveness and productivity.
- Proofs of concepts, proto-types, and demos for commercialisation.
Investment for Belfast
The programme is expected to attract over £2 million of investment from the private and public sectors.
Collaborative partners
- Telecoms and cloud industry
- Belfast creative digital sector
- Belfast Region City Deal
- Future Screens NI
- Belfast Stories
- Digital Catapult UK
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges
- 4. A vibrant innovation economy
- 6. Financing, procurement and adoption
- 7. Technology infrastructure
Supporting Advanced Urban Services
We are working directly with the council’s departments and other public bodies to build greater innovation capacity, and to co-design interventions to establish advanced urban services for a twenty-first century city.
We will build opportunities to harness the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund to encourage SMEs across the region to work with our service managers on significant council challenges related to waste, net zero and the future of our city centre.
We are also developing a suite of innovation materials that brings together practical toolkits and playbooks in areas such as innovative public procurement, agile service design, urban data analytics and triple helix collaboration models.
As part of the All Ireland Smart Cities Forum, Mastercard’s City Possible, the Global Smart Cities Alliance, and UK Smart Cities Network, Belfast is also able to avail of best practice and model urban innovation policies from across the world.
Delivering for Belfast
- More effective, efficient and enhanced council services.
- More effective routes to procuring innovation.
- Capturing best practice in public service innovation from around the globe.
Investment for Belfast
- A proportion of the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund.
- Collaborative innovation funding from Innovate UK and elsewhere.
- Collaborative innovation investment from industry.
Collaborative partners
- All Ireland Smart Cities Forum
- Belfast City Council departments
- Belfast Region City Deal
- National and international smart city partnerships
Pillar contribution
- 2. Urban challenges
- 6. Financing, procurement and adoption
5.The Belfast Smart District
The physical location for our programme of work is the Belfast Smart District. Co-terminus with the city centre, the District is the place where we will foster the conditions for collaborative innovation focused on Belfast’s major urban challenges.
This is the place where we want partners to work with us on novel solutions to these challenges. And, when they succeed, we want to make sure these solutions are scaled or replicated across our city and region.
We are working with partners to leverage their planned investments for the city centre; to grow state-of-the-art connectivity there; to attract public and private innovation funding, and to work with asset owners and public offices to generate opportunities for experimentation, testing, and the development of advanced urban solutions that directly address real-world challenges. Our approach is to make the Smart District the natural home for our innovators and researchers.
The Smart District will be the place where Belfast can demonstrate and showcase its talent and ingenuity to the world.
Belfast Smart District area
Key investments provide a rich environment for the delivery of the Smart Belfast programme.
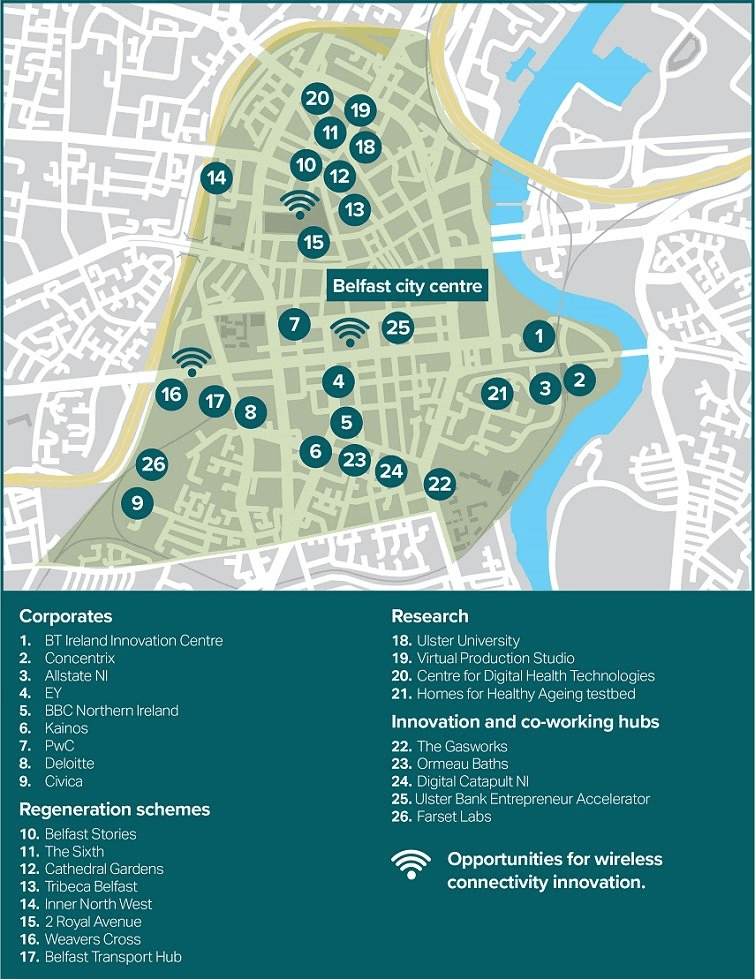
The areas and organisations highlighted in the Belfast Smart District map area are:
Corporates
1. BT Ireland Innovation Centre
2.Concentrix
3. Allstate NI
4.EY
5. BBC Northern Ireland
6.Kainos
7. PwC
8.Deloitte
9. Civica
Regeneration schemes
10. Belfast Stories
11. The Sixth
12. Cathedral Gardens
13. Tribeca Belfast
14. Inner North West
15. 2 Royal Avenue
16. Weavers Cross
17. Belfast Transport Hub
Research
18. Ulster University
19. Virtual Production Studio
20. Centre for Digital Health Technologies
21. Homes for Healthy Ageing testbed
Innovation and co-working hubs
22. The Gasworks
23. Ormeau Baths
24. Digital Catapult NI
25. Ulster Bank Entrepreneur Accelerator
26. Farset Labs
Opportunities for wireless connectivity innovation.

Corporates
- BT Ireland Innovation Centre
- Concentrix
- Allstate NI
- EY
- BBC Northern Ireland
- Kainos
- PwC
- Deloitte
- Civica
Regeneration schemes
- Belfast Stories
- The Sixth
- Cathedral Gardens
- Tribeca Belfast
- Inner North West
- 2 Royal Avenue
- Weaver's Cross
- Belfast Transport Hub
Research
- Ulster University
- Virtual Production Studio
- Centre for Digital Health Technologies
- Homes for Healthy Ageing testbed
Innovation and co-working hubs
- The Gasworks
- Ormeau Baths
- Digital Catapult NI
- Ulster Bank Entrepreneur Accelerator
- Farset Labs
Opportunities for wireless connectivity innovation
Corporates
BT Ireland Innovation Centre
A £28million R and D centre with Ulster University, focused on advanced research in IoT, AI, 5G and data analytics.
Concentrix
The US business services giant has three offices in Northern Ireland, providing a range of customers experience and digital solutions to a range of sectors across the world.
Allstate NI
Northern Ireland’s largest IT company employs over 2,400 people and provides expertise in areas such as data, cybersecurity and FinTech.
EY
The international consultancy has a significant Belfast practice which is home to its UK and Ireland Delivery Centre.
BBC Northern Ireland
As well as operating TV, radio and online broadcasting services, BBC NI is involved in a range of initiatives that support the creative industries sector and skills development in Northern Ireland.
Kainos
Providing digital technology solutions for businesses and organisations, Kainos, Northern Ireland’s first homegrown FTSE 250 firm will relocate to its new headquarters at Bankmore Square by 2026.
PwC
PwC’s Belfast office is its largest regional office outside London and home to some of its global centres of excellence including a £40 million Advanced Research and Engineering Centre.
Deloitte
Professional services company Deloitte delivers a range of technology and digital transformation services with expertise in areas such as robotics, cybersecurity and FinTech.
Civica
Based at Weaver's Court, Civica delivers digital transformation initiatives for a range of organisations including the public sector.
Regeneration schemes
Belfast Stories
A signature £100million cultural visitor destination in the heart of the city featuring: the Belfast Story contemporary visitor experience; the Belfast Film Centre; creative and digital skills spaces; inspirational architecture and civic spaces.
The Sixth
Located in the former Belfast Telegraph building, this mixed-use scheme includes 30,000 square metres of commercial space, state-of-the-art workspace, and active ground floor uses such as cafés, restaurants and retail.
Cathedral Gardens
A multi-million pound redevelopment will transform this area into a unique world-class public space with an urban forest, public art, interactive audio-visual water and lighting features, outdoor dining areas and a range of play features for children.
Tribeca Belfast
A prime 12-acre city centre regeneration scheme, investing £500 million to deliver 1.5 million square feet of residential, office, retail, hospitality and cultural space.
Inner North West
A 42-acre city centre site incorporating residential, commercial, retail and leisure, together offering a sustainable and integrated urban living environment.
2 Royal Avenue
A city centre space with a new approach to experiential tourism and culture in the city, hosting a wide variety of events and experiences delivered in partnership with the city’s cultural sector.
Weaver's Cross
A £380 million transport led regeneration project which will link a new high-capacity transport hub with mixed-use development opportunities.
Belfast Transport Hub
Replacing the existing Europa and Great Victoria Street bus and rail stations, the new Belfast Grand Central Station will be the largest integrated transport facility on the island of Ireland when it opens in 2025.
Research
Ulster University
A £250 million investment in Ulster University’s new Belfast campus, delivering a world-class facility to 15,000 students and staff.
Virtual Production Studio
The £1.6 million state-of-the-art studio at Ulster University provides access to cutting edge production and VFX facilities which are unique to the island of Ireland.
Centre for Digital Health Technologies
A £45 million Ulster University centre for digital healthcare and associated living labs in the areas of cardiology, diabetes, respiratory and stroke.
Homes for Healthy Ageing testbed
Trialling innovative approaches to healthy ageing, this testbed in the Markets Area is part of the £2.5 million Connected Places Catapult ‘Homes for Healthy Ageing’ Programme.
Innovation and co-working hubs
The Gasworks
Home to the Ormeau Business Park, this entrepreneurial community includes emerging businesses, spin-outs and start-up companies.
Ormeau Baths
Originally a Victorian bathhouse, it's now an award-winning co-working space for some of our brightest and best tech start-ups. Supported by over 20 global partners and home to Ignite NI and Energia.
Digital Catapult NI
The NI regional centre of Digital Catapult UK connects industry and academia to build innovative partnerships and helps organisations to adopt advanced digital technologies.
Ulster Bank Entrepreneur Accelerator
Based at Ulster Bank’s iconic Belfast headquarters, the hub helps businesses access new markers, funding and talent.
Farset Labs
A community-funded charity, this co-working space provides a hub of creativity, technological experimentation and entrepreneurship.
Key components of a Smart District
1. A challenge rich environment
The district should be a place where innovators can solve problems for the city. It is the laboratory for real-world experimentation, trials and testbeds. It should help bring ideas out of the lab and into the streets. And then onwards for adoption across the entire city and region.

2. Size
The geography needs to be large enough to deliver substantial projects, but not so large that resources for management and delivery are spread too thinly.
.jpg?width=300&height=214)
3. Opportunity and investment
It must be a place where substantial public and private investments are being planned. And where organisations are already delivering projects and programmes.

4. People
Innovation is all about people. The district needs to be a place where people want to meet, live, work and play. This generates opportunities to share knowledge, exchange ideas and invest together.

5. Innovation actors
The district needs to be close to universities and colleges, SME incubators, and enterprises with a commitment to investing in local innovation.

6. Data and connectivity
The backbone and fundamental resource for digital innovation. State-of-the-art fibre and advanced wireless connectivity should be within the reach of any innovator. A place where huge quantities of data are generated, stored and shared - in ways that are transparent, secure, trusted and accessible.

7. Key transport connections
The Smart District should be at the centre of public and active transport connections, to help foster the exchange of ideas, talent and opportunities.

8. A showcase to the world
The Smart District is our showcase to the world, demonstrating our ability to innovate and build great products and services. And to provide an example of how a city can address the great urban challenges of the 21st century.

Building the Belfast Smart District
A successful Smart District has a number of features that have to be nurtured and developed. Alongside our core programme, the City Innovation Office will be working with partners on these aspects:
1. Build governance and operational capacity
The District requires a quadruple helix partnership, between industry, academia, public bodies and citizens, to set goals, to help define priorities and the project portfolio, and to ensure an approach that maximises the range of opportunities. This group, convened by Belfast City Council, will interconnect with the work of Innovation City Belfast, the Bolder Vision steering group, and others to ensure the District contributes to wider economy and societal goals.
Operationally, the Smart District will be supported by Belfast City Council’s City Innovation Office.
Key tasks
- Establish the Smart District governance and delivery arrangements.
- Develop detailed operational and resourcing plans.
- Develop a reporting and insights model to track the impact of the District.
- Establish an agile operational model to leverage resources from key partners and funders.
2. Telling our story
Strong, engaged partnerships are at the heart of a Smart District. Within Belfast city centre there is an existing innovator community and a complex range of other stakeholders, investors, businesses, universities and colleges, service providers, residents and visitors. Much of the early work in the District involves engaging with these stakeholders on shared opportunities, challenges, and the potential for collaboration.
We also want to share the learning and the successes from our District with the wider city, region and the world. We want the District to be a place where innovators (from large international enterprises to two-person start-ups) want to be.
Key tasks
- District level engagement programme with stakeholders with a focus on an opportunity audit.
- Deliver a marketing and communications campaign to share the ambition for the District and its contributory relationship with the city’s wider ambition.
- Work with Invest NI and others to utilise the District in the support of the wider promotion of the city as a place to invest.
- Build an online learning and playbook resource to support the wider replication and adoption of Smart District successes across the city and region.
3. Establish a sustainable financing model
Belfast City Council has committed a core operational resource for the District. However, longer term sustainability will be dependent on a blend of funding and financing mechanisms. Initially, the core investments will come from the Digital pillar of the Belfast Region City Deal which will make substantial funding available for challenge funds and to support necessary infrastructure investments.
We will also leverage the substantial public and private sector capital investments planned for the city and seek to influence their priorities to enhance the District. For example, other cities have worked with developers to ensure that new builds or street works can facilitate the rapid deployment of fibre and wireless connectivity.
There is also substantial public funding for digital innovation available from UK Research and Innovation, UK Department of Digital, Culture, Media and Sport and Horizon Europe. A functional Smart District becomes a serious attractor for such funding by adding weight to project applications from academia and industry.
Over the longer term, some smart districts have established special purpose vehicles that are able to use a mix of private and public investment to create a self-sustaining smart district programme. Belfast will explore this option.
Key tasks
- Design opportunities to leverage the £34 million Innovation for Societal Impact Fund.
- Design opportunities to leverage the £40 million infrastructure Enabling Fund.
- Opportunity analysis with our partners, particularly our local universities, of forthcoming Government funding opportunities against Smart District objectives.
- Engagement with District investors (both public and private) on co-investment opportunities.
- Develop an intelligence hub - for use by all partners including SMEs and public sector to navigate the complexity of the funding landscape.
Funding for innovation
The Smart District will draw upon a range of funding sources, including the Belfast Region City Deal, Innovate UK, UKRI, Horizon Europe and others to drive greater investment in innovation. Support mechanisms will be designed to encourage SMEs, innovators, academia and the public sector to collaborate on smart district challenges - while at the same time supporting innovation along the Translational Research Levels. Complementing existing support, this may include:
- Start-up challenges to help build early-stage innovators’ capacity and to support their entry to market. Challenges are broad to attract a wider pool of innovators, with staged funding to funnel and target investment support.
- District-centred prizes bring the District’s stakeholders and innovators together to develop solutions and focus more on early stage innovations that need to be tested and developed.
- Spotlight prizes focusing on urban problems that have been neglected. Usually existing solutions to these problems or issues lack nuanced understanding of end users’ needs.
- Testbed prizes stimulate innovation in support of policy or regulatory objectives and to inform future policy in the District. These will be of particular interest to city planners and regulators with an interest in deploying innovation across the city.
- Breakthrough prizes are used to create transformative solutions to difficult problems. They are often ambitious projects with tightly-defined goals seeking technological solutions, offering larger funding pots and longer time-frames.
- Scaling prizes scale transformative solutions to achieve wider impact. These typically target a small pool of innovators and set quantifiable targets to reward scaling to kickstart a potential market.
- Small Business Research Initiative - (SBRI) provides a further mechanism for public sector bodies to explore innovation solutions in a pre-commercial procurement phase. Their aim is to support the development of new solutions not available on the market.
4. Supporting citizen co-design
The role of the citizen is particularly important in the success of urban innovation. The District, and the programme associated with it, cannot be imposed on the citizens who live or work in the city centre.
Projects are more effective and better targeted if they are co-designed with the end-user. This co-design approach adopts some techniques from the software industry, but also requires community capacity building and tailored engagement to ensure that projects are trusted and meet the people’s needs.
This is not about training in technology or software development. It is about understanding challenge definition, the innovation process, and the opportunities and issues associated with smart city technologies. The approach can act as an ‘on-ramp’ to more formal skills development and education opportunities for individuals and communities.
Key tasks
- The design and delivery of the Citizen Opportunities for Digital Innovation (CODI) programme.
- Work with city partners to develop a shared user-centred methodology to support the design of significant Smart District projects.
- Create opportunities to inform the wider skills agenda of key partners.
5. Enhancing digital and data connectivity
We want to make the Smart District one of the most digitally connected spaces in the world. The aim is to offer easily accessible, ubiquitous, low-cost, low latency, high capacity connectivity, on an architecture that encourages innovation and discourages vendor lock-in and legacy systems.
This is a challenging undertaking in a dense urban environment, but we believe that with necessary private and public sector investments, we can make the District the primary location for digitally connected innovators.
The District is a data-rich environment. Our partners, projects and technologies will generate huge quantities of novel data. Such data becomes an important catalyst for innovation if it can be made available to partners in a safe, transparent and open fashion. Working from a set of agreed data principles, we aim to work with partners to establish a data architecture and urban data platform for the city.
Key tasks
- Deliver a Belfast Region City Deal business case for investment to support advanced wireless networking across the District.
- Work with public sector and other partners on a ‘Site as a Service’ product that ensures relevant physical assets are available for the rapid deployment of connectivity.
- Deliver a feasibility study and Belfast Region City Deal business case for £5 million investment in an urban data platform for the District and wider region.
- Develop and adopt a shared technology architecture with partners to support an open architecture that fosters collaboration on open innovation.
- Work with partners to pilot, showcase and scale wireless connectivity demonstrators in the District.
- Maximise the investments in Belfast’s Local Full Fibre Network (LFFN).
6. Sandbox and testbed environment
The District is the go-to location for universities and businesses to develop proofs of concepts, test proto-types and trial new products and services. It is a place where commercial solutions are deployed and showcased to the city and the world.
To do so, we are working with the universities, businesses, asset owners, regulators, health and safety organisations and others to identify, reduce or remove the barriers that often make such work difficult in the real-world environment. We are also establishing cohorts of engaged end-users who can work with innovators to co-design and participate in the development of new urban solutions.
Key tasks
- Work with institutions, such as the UK Information Commissioner’s Office, Ada Lovelace Institute, Financial Conduct Authority, Health and Safety Executive, university ethics committees and others to develop a supportive urban ‘sandbox’ environment.
- Deliver engagement and capacity building programmes to develop citizen cohort groups.
- Work with public sector partners on a joint barrier-busting resource that will seek to remove unnecessary administrative burdens on innovation projects.
7. Replication, scaling, and showcase
While the District is the initial focus for urban innovation, the longer-term aim is to take the hard-won learning and successes from projects developed in the District and scale or replicate them across the wider city and region. So, for example, if a mobility project is shown to have encouraged greater uptake of active travel in the District, then the project can be adopted by agencies across Belfast. We might also want to showcase this success at a national or international level, particularly if it’s associated with a novel solution that can be commercialised by the SME that developed it.
For this to work, we need mechanisms to track and capture details of the project portfolio. We will work with city partners to share learning. We are also establishing promotional channels to ensure that learning and successes are celebrated and showcased across the world.
The ‘first customer’ is an important role for SMEs that have developed a novel product. Our aim is to work with our public sector partners to encourage innovative procurement of products developed in the District.
Key tasks
- Put in place a knowledge capture mechanism for District projects that will be available to all stakeholders.
- Develop an innovative procurement playbook for public sector partners with Connected Places Catapult and Invest NI.
- Work with Invest NI, Innovation City Belfast and others on a joint marketing plan to showcase the District and the work of its researchers and SMEs.
6. City Innovation Office
The City Innovation Office was established by Belfast City Council to ensure that innovative thinking and approaches are placed at the heart of the strategies and plans for the city. The office is made up of experienced innovation brokers and specialists across a range of thematic and policy areas. It works across all of the departments in the council and drives a range of cross sector collaborative programmes and partnerships.
Get involved
If you would like to get involved in our urban innovation ambitions for Belfast, we're keen to work with you, so let's collaborate to innovate.
Telephone: +44 (0)28 9032 0202
Email: smartbelfast@belfastcity.gov.uk
Smart City Belfast (link opens in new window)
#smartbelfast
Governance
Belfast Region City Deal
Contributing to the region’s digital innovation priorities and maximising opportunities with other City Deal investments.
City Innovation Office
Maximising the contribution that digital innovation makes to the city’s economic, social and environmental strategic priorities.
Innovation City Belfast
Working with the city’s innovation partnership to maximise the impact of the Smart Belfast programme.
Industry engagement
Key partners
A number of organisations have been important in the development of this framework. They include:
- Belfast Harbour
- Belfast Region City Deal Executive Board
- Catalyst
- Connected Places Catapult
- Digital Catapult NI
- Eindhoven Brainport
- European Network of Living Labs
- Global Institute on Innovation Districts
- Innovation City Belfast
- Institute of Innovation and Public Purpose
- Invest NI
- Nesta
- NI Department for the Economy Innovation Team
- Queen’s University Belfast
- Ulster University
Measuring our impact
Working with our innovation partners, we are establishing an evaluation framework that measures the impact of our investments, and the contribution that urban innovation is making to the city's 'missions'.
We are particularly interested in the novel use of digital technology to reduce the reporting burden of SME partners while providing timely, fine grain insights that can inform agile programme design and delivery.
Our approach is building on the work of Innovate UK, and University College London’s Institute for Innovation and Public Purpose, and on the Belfast pilot project, ‘Measuring the Impact of Public Policy interventions’.
